# 查看conda虚拟环境列表 conda env list # 删除虚拟环境 conda remove -n my_first_env --all # 创建虚拟环境 conda create --name my_first_env python=3.6 # 进入虚拟环境 conda activate my_first_env
分类: python
Python获取硬件信息(硬盘序列号,CPU序列号)
pip install wmi pip install pywin32
import wmi
c = wmi.WMI()
# # 硬盘序列号
for physical_disk in c.Win32_DiskDrive():
print(physical_disk.SerialNumber)
# CPU序列号
for cpu in c.Win32_Processor():
print(cpu.ProcessorId.strip())
# 主板序列号
for board_id in c.Win32_BaseBoard():
print(board_id.SerialNumber)
# mac地址
for mac in c.Win32_NetworkAdapter():
print(mac.MACAddress)
# bios序列号
for bios_id in c.Win32_BIOS():
print(bios_id.SerialNumber.strip())Python操作Redis
python中删除某个元素的3种方法
1.remove: 删除单个元素,删除首个符合条件的元素,按值删除
举例说明:
>>> str=[1,2,3,4,5,2,6]
>>> str.remove(2)
>>> str
[1, 3, 4, 5, 2, 6]
2.pop: 删除单个或多个元素,按位删除(根据索引删除)
>>> str=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6]
>>> str.pop(1) #pop删除时会返回被删除的元素
1
>>> str
[0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
>>> str2=['abc','bcd','dce']
>>> str2.pop(2)
'dce'
>>> str2
['abc', 'bcd']
3.del:它是根据索引(元素所在位置)来删除
举例说明:
>>> str=[1,2,3,4,5,2,6]
>>> del str[1]
>>> str
[1, 3, 4, 5, 2, 6]
>>> str2=['abc','bcd','dce']
>>> del str2[1]
>>> str2
['abc', 'dce']
除此之外,del还可以删除指定范围内的值。
>>> str=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6]
>>> del str[2:4] #删除从第2个元素开始,到第4个为止的元素(但是不包括尾部元素)
>>> str
[0, 1, 4, 5, 6]
del 也可以删除整个数据对象(列表、集合等)
>>> str=[0,1,2,3,4,5,6]
>>> del str
>>> str #删除后,找不到对象
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#27>", line 1, in <module>
str
NameError: name 'str' is not defined
注意:del是删除引用(变量)而不是删除对象(数据),对象由自动垃圾回收机制(GC)删除。
补充: 删除元素的变相方法
s1=(1,2,3,4,5,6)
s2=(2,3,5)
s3=[]
for i in s1:
if i not in s2:
s3.append(i)
print 's1-1:',s1
s1=s3
print 's2:',s2
print 's3:',s3
print 's1-2:',s1Python 时间格式化
# strftime()方法语法: time.strftime(format[, t]) # 参数 # format -- 格式字符串。 # t -- 可选的参数t是一个struct_time对象。 """ python中时间日期格式化符号: %y 两位数的年份表示(00-99) %Y 四位数的年份表示(000-9999) %m 月份(01-12) %d 月内中的一天(0-31) %H 24小时制小时数(0-23) %I 12小时制小时数(01-12) %M 分钟数(00=59) %S 秒(00-59) %a 本地简化星期名称 %A 本地完整星期名称 %b 本地简化的月份名称 %B 本地完整的月份名称 %c 本地相应的日期表示和时间表示 %j 年内的一天(001-366) %p 本地A.M.或P.M.的等价符 %U 一年中的星期数(00-53)星期天为星期的开始 %w 星期(0-6),星期天为星期的开始 %W 一年中的星期数(00-53)星期一为星期的开始 %x 本地相应的日期表示 %X 本地相应的时间表示 %Z 当前时区的名称 %% %号本身 """
python中把’\xe5\xb7\xa5\’转成汉字格式
解决方法:
在字符串后面加上.decode("utf-8"),问题解决
如:res.content.decode("utf-8")Python函数
# 列表
# 查找元素在列表中位置
p=list.index(value) # list为列表的名字 value为查找的值 p为value在list的位置
# Python中bytes与字符串的相互转化
# bytes转字符串方式一
b=b'\xe9\x80\x86\xe7\x81\xab'
string=str(b,'utf-8')
print(string)
# bytes转字符串方式二
b=b'\xe9\x80\x86\xe7\x81\xab'
string=b.decode() # 第一参数默认utf8,第二参数默认strict
print(string)
# bytes转字符串方式三
b=b'\xe9\x80\x86\xe7\x81haha\xab'
string=b.decode('utf-8','ignore') # 忽略非法字符,用strict会抛出异常
print(string)
# bytes转字符串方式四
b=b'\xe9\x80\x86\xe7\x81haha\xab'
string=b.decode('utf-8','replace') # 用?取代非法字符
print(string)
# 字符串转bytes方式一
str1='逆火'
b=bytes(str1, encoding='utf-8')
print(b)
# 字符串转bytes方式二
b=str1.encode('utf-8')
print(b)
# python3 字典、列表、数组和字符串之间的相互转化
# 字典
dict_1 = {'1': 'a', '2': 'b', '3': 'c'}
print(dict_1) # 打印字典
print(type(dict_1)) # 打印新赋值的字典的类型
print(str(dict_1), end='字符串\n') # 把字典转化成字符串后打印
print(tuple(dict_1), end='元组\n') # 把字典转化为元组后打印
print(list(dict_1), end='列表\n') # 把字典转化为列表后打印
# 元组
tuple_1 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
print(tuple_1) # 打印元组
print(type(tuple_1)) # 打印新赋值的元祖的类型
print(str(tuple_1), end='字符串\n') # 把元组转化成字符串后打印
print(list(tuple_1), end='列表\n') # 把元组转化为列表后打印
# 元组不可转化为字典
#列表
list_1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print(list_1) # 打印列表
print(type(list_1)) # 打印新赋值的列表的类型
print(str(list_1), end='字符串\n') # 把列表转化成字符串后打印
print(tuple(list_1), end='元组\n') # 把列表转化为元组后打印
#字符串
string_1 = '(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)'
print(string_1) # 打印字符串
print(type(string_1)) # 打印新赋值的字符串
print(tuple(eval(string_1)), end='元组\n') # 把字符串转化成元组后输出
print(list(eval(string_1)), end='列表\n') # 把字符串转化成列表后输出
# 只有特殊字符串才能转化为字典
string_2 = '{"name":"tom","age":6}'
print(string_2) # 打印新赋值的字符串
print(type(string_2)) # 打印新赋值的字符串的类型
print(eval(string_2), end='字典\n') # 把字符串转化为字典后打印
python获得在线视频时长
# coding:utf-8
import struct
import requests
class Mp4info:
def __init__(self, file):
self.file = file
self.seek = 0
self.duration = 0
self.s = requests.session()
self.timeout = 6
self.s.headers = {
'Connection': 'keep-alive',
'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8',
'Accept-Encoding': 'gzip, deflate',
'Accept-Language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en-US;q=0.8,en;q=0.7',
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_13_4) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/66.0.3359.139 Safari/537.36'
}
# 设置请求头 set request header
# 传入的seek表示代表需要跳过的字节数量 use seek to skip initial data
# 在这里进行判断是为了后续获取视频的宽高信息预留的 the condition here is for reserving space for getting the media data
def _set_headers(self, seek, type):
if type in ['moov', 'duration']:
self.s.headers['Range'] = 'bytes={}-{}'.format(seek, seek + 7)
def _send_request(self):
try:
data = self.s.get(url=self.file, stream=True,
timeout=self.timeout).raw.read()
except requests.Timeout:
raise '连接超时:超过6秒(默认)服务器没有响应任何数据!' # timeout 6 seconds, the server fails to respond and assumes there is no data
return data
def _find_moov_request(self):
self._set_headers(self.seek, type='moov')
data = self._send_request()
size = int(struct.unpack('>I', data[:4])[0])
flag = data[-4:].decode('ascii')
return size, flag
def _find_duration_request(self):
# 4+4是moov的大小和标识,跳过20个字符,直接读到time_scale,duration # 4+4 is the first 8 characters denoting charset, skip the next 20 to time_scale and duration
self._set_headers(seek=self.seek+4+4+20, type='duration')
data = self._send_request()
time_scale = int(struct.unpack('>I', data[:4])[0])
duration = int(struct.unpack('>I', data[-4:])[0])
return time_scale, duration
def get_duration(self):
while True:
size, flag = self._find_moov_request()
if flag == 'moov':
time_scale, duration = self._find_duration_request()
self.duration = duration/time_scale
return self.duration
else:
self.seek += size
if __name__ == '__main__':
url = 'https://vd2.bdstatic.com/mda-mfqszq3mzd845q23/1080p/cae_h264/1624620686306577424/mda-mfqszq3mzd845q23.mp4?v_from_s=hkapp-haokan-tucheng&auth_key=1625478247-0-0-6baa0019344f9a31db76ddb4be3909e5&bcevod_channel=searchbox_feed&pd=1&pt=3&abtest=3000165_1'
file = Mp4info(url)
a = file.get_duration()
print(a)
原文链接: https://blog.csdn.net/longjuanfengzc/article/details/103006691
Django 安装并创建空项目
1.pip安装Django
pip install django==2.2.4
2.创建一个名为 welcome 的Django项目
django-admin startproject welcome
3. 进入 welcome 文件夹 启动项目
cd welcome # 进入welcome文件夹 python manage.py runserver # 启动服务器默认监听8000端口 python manage.py runserver 5000 # 启动服务器并手动指定监听5000端口
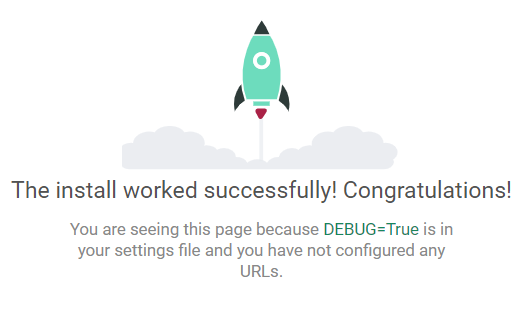
4.打开 127.0.0.1:8000 出现小火箭说明项目创建成功
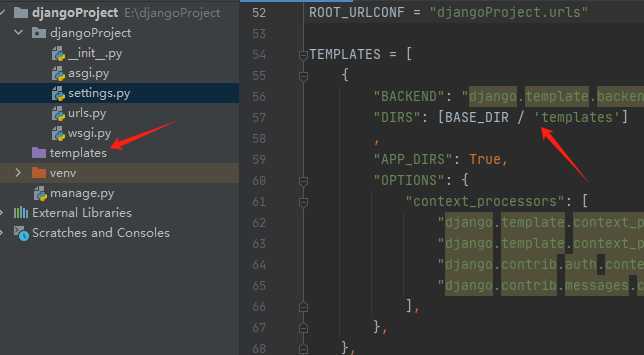
5.项目目录结构

6.项目创建成功的准备工作
- 新建项目删除templates文件夹,并且修改setting这里的设置为[]
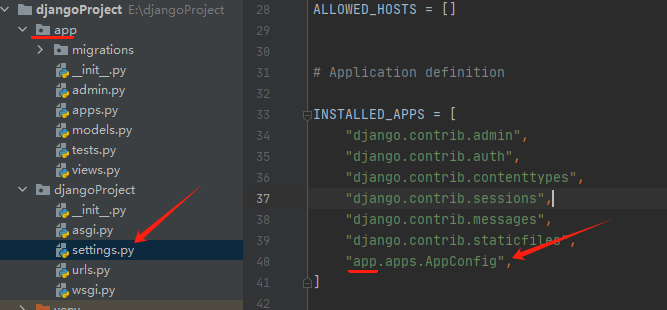
7.创建一个空的APP
# 创建一个叫app的APP,下图中创建的是叫app01,不重要 py manage.py startapp app

8.去settings注册这个app
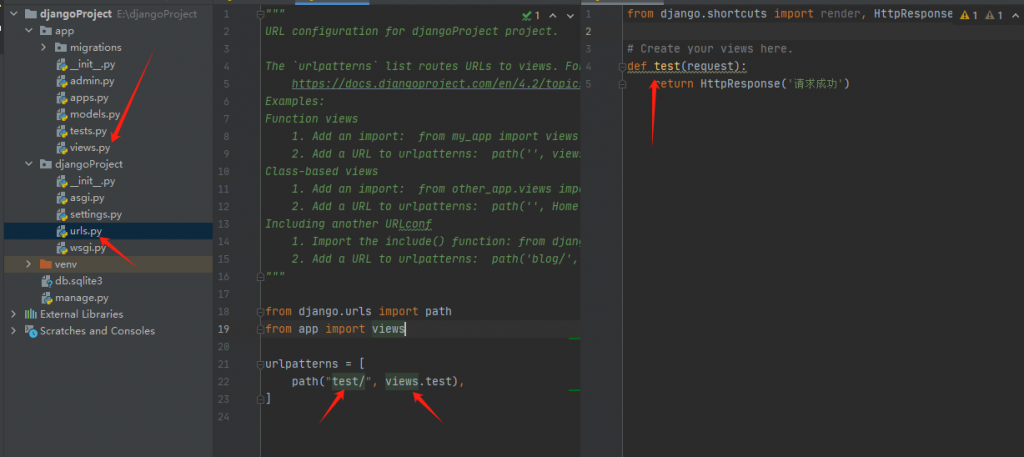
9.启动django命令
py manage.py runserver 8000
10.编写一个普通的请求
python pip 安装
安装cv2 执行语句
pip install opencv-python pip3 install opencv-python==4.4.0.42
安装PIL 执行语句
pip install pillow
安装 win32gui, win32ui
pip install -i https://pypi.doubanio.com/simple/ pywin32